LC-MS/MS를 이용한 돼지 근육조직 중 dl-methylephedrine hydrochloride의 잔류 분석법 개발
Development of an analytical method for the determination of dl-methylephedrine hydrochloride in porcine muscle using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry
Article information
Trans Abstract
This study examined the residue of dl-methylephedrine hydrochloride (MEP) on the muscle of pigs administered orally with MEP 12 g/ton feed for seven consecutive days. Twenty healthy cross swine were administered MEP. Four treated animals were selected arbitrarily to be sacrificed at 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 days after treatment. MEP residue concentrations in the muscle were determined by liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. The drug was extracted from muscle samples using 10 mM ammonium formate in acetonitrile followed by clean-up with n-hexane. The analyte was separated on an XBridgeTM hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography column using 10 mM ammonium formate in deionized distilled water and acetonitrile. The correlation coefficient (R2) of the calibration curve was 0.9974, and the limits of detection and quantification were 0.05 and 0.15 μg/kg, respectively. The recoveries at three spiking levels were 94.5–101.2%, and the relative Standard Deviations was less than 4.06%. In the MEP-treated group, MEP residues on one day post-treatment were below the maximum residue limit in the muscle. The developed method is sensitive and reliable for the detection of MEP in porcine muscle tissues. Furthermore, it exhibits low quantification limits for animal-derived food products destined for human consumption.
서 론
최근, dl-염산메틸에페드린(dl-methylephedrine hydrochloride, MEP)은 돼지 흉막폐렴 치료에 다른 약제들과 병용해서 사용되고 있어서[1], 돼지의 근육 조직에서 MEP의 잔류 분석이 요구되고 있다.
현재, MEP는 진해제로서 인체의 각종 감기약에 사용되고 있다[2]. 또한, MEP는 교감신경흥분 작용을 갖고 있어서 기관지확장제로 사용되고 있으며, 기침과 코막힘 완화를 위한 복합조제약물로 사용되고 있다[3]. MEP는 ephedrine의 유도체로서, ephedrine과 비교하여, 중추신경계 흥분작용이 거의 없고, 혈압상승 작용은 1/10이며, 기관지확장작용은 약하지만 항히스타민 작용은 강한 것으로 알려져 있다[4]. Ephedrine은 한약재 마황(Ephendra sinica)의 주성분인 alkaloids의 30-90%를 차지하고 있는 물질로서, 아드레날린과 유사한 효과를 갖는 교감신경계 자극성 아민이다[5,6]. 이러한 작용으로 인해, ephedrine은 일반적으로 식품보조제로서 체중감소와 에너지 증진을 위해 혹은 충혈완화제로 섭취되고 있다[7]. 하지만, 미국의 FDA는 ephedrine의 간독성, 심장 박동수와 혈압 증가, 심근경색 등과 같은 심각한 부작용으로 인해 2003년 이후로 식품보조제로 사용하는 것을 전면적으로 금지하였다[8-10]. 반면에, MEP와 같은 합성 alkaloids는 의약품으로 시중에 판매되고 있다[11].
식품의약품안전처의 ‘식품의 동물용의약품 잔류허용기준’에 따르면[12], MEP의 최대잔류허용기준(maximum residue limit)은 소와 돼지의 근육에서 모두 0.01 mg/kg으로 설정되어 있다.
앞선 연구들에서 보고된 MEP의 잔류분석법에는, 비색법[2], 고속액체크로마토그래피법(high-performance liquid chromatography) [13], 기체크로마토그래피법(gas chromatography) [14], 액체크로마토그래피-질량분석법(liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry, LC-MS/MS) [15] 등이 있는데, 이들 분석법들은 주로 인체 복합처방약에서 MEP의 정량분석 혹은 인체 혈액 중에서 MEP의 약동학적 분석을 목적으로 개발된 방법들이다. 하지만, MEP의 경구투여 후, 돼지의 식용조직에서의 MEP의 잔류분석법에 대한 연구는 Zhang 등의 연구[16]를 제외하고는 거의 존재하지 않고 있다. 따라서 본 연구에서는 MEP의 경구투여 후, 돼지 근육 조직에서 MEP 잔류 분석과 MEP의 안전휴약기간 설정을 목적으로 수행하였다.
재료 및 방법
시약 및 재료
MEP 함유 시험약제(MEP, 12 g/kg)는 ㈜중앙바이오텍(안산)으로부터 제공받아 시험에 사용하였으며, MEP 표준품(순도, ≥ 98%)은 ㈜ 켐트로스(안산)로부터 구입하였으며, ammonium formate와 acetonitrile은 Merck KGaA (Darmstadt, Germany)로부터 구입하였다.
표준원액 및 표준용액의 조제
MEP 표준품 1.0 mg을 저울로 정밀히 달아 1,000 mL 정량플라스크에 넣고, 메탄올을 사용하여 1.0 mg/L이 되도록 표준원액을 조제하였다. 조제한 표준원액을 메탄올을 사용하여 단계적으로 희석하여 0.1, 0.5, 1.0, 5.0, 10.0 ng/mL의 표준용액을 각각 준비하여, 갈색 유리병에 담아 사용 전까지 4°C 냉장실에 보관하였다.
실험동물 및 시료채취
돼지 근육 중 MEP의 잔류 농도를 확인하기 위해, 건강한 20마리의 돼지(체중, 40-50 kg)를 대상으로 시험을 수행하였다. 4마리는 무투여 대조군으로 하였으며, 16마리에게는 MEP를 사료 톤 당 12 g을 혼합하여 7일 동안 연속해서 투여하였다. MEP 투여군은 MEP 투여 후, 1, 2, 3, 5일째에, 무투여 대조군은 MEP 투여 후 1일째에 각각 4마리씩을 안락사 시킨 다음, 근육 조직(대퇴이두근, 좌우 각각 1곳씩)을 200 g 정도씩 채취하여, 분석에 사용하기 전까지 -20°C 냉동고에 보관하였다.
시료 전처리
시료 전처리를 위해, 균질화된 돼지 근육 시료 5g을 50 mL 원심분리관에 넣고 10 mM ammonium formate를 함유한 acetonitrile 20 mL을 가하여 15분간 진탕 혼합한 후, 4°C, 2,600 ×g에서 15분간 원심 분리하였다. 원심분리 후, 상징액을 50 mL 원심분리관에 취하고 여기에 20 mL 헥산을 넣어 10분간 진탕 혼합한 다음, 4°C, 2,600 ×g에서 15분간 원심 분리하였다. 원심분리 후, 상징액을 15 mL 원심분리관에 담아 40°C에서 0.5 mL이 될 때까지 질소 가스로 농축시킨 다음, acetonitrile 1.5 mL을 가한 뒤 재분산하고 4°C, 15,000×g에서 10분간 원심분리하였다. 원심분리 후, 상징액을 0.45 μm polytetrafluoroethylene membrane filter (Millipore Merck Korea, Korea)로 여과시킨 것을 시험용액으로 하였다.
기기분석 조건
돼지 근육 시료 중 MEP 분석을 위하여, 앞선 연구들[16,17]을 참고하여, LC-MS/MS (API4000, AB SCIEX, Canada)를 사용하였으며, 본 LC-MS/MS의 LC system은 Agilent 1260 series (Agilent Technologies, Germany), 분석용 column은 X bridge HILIC (2.1 × 100 mm, 3.5 μm, Waters, USA)을 사용하였으며, column 온도는 30°C를 유지하였다. 또한, 이동상 A와 B는 각각 10 mM ammonium formate와 acetonitrile로 하여 10:90으로 사용하였으며, flow rate은 0.3 mL/min으로 하였고, 크로마토그래프상 tota l running time은 15분으로 하였다. 질량분석기는 Triple Quad 4500 System (Agilent Technologies)을 사용하였다. MEP의 이온화법은 electro-spray ionization positive로 MS조건을 최적화 하였으며, multiple reaction monitoring transition (m/z)으로 180.1 → 162.1을 사용하였다.
분석법 검증
앞서 준비한 표준용액(0.1-10.0 ng/mL)을 이용하여 검량곡선을 작성하였으며, 검량선의 직선성을 확인하기 위해 상관계수(coefficient of correlation, R2)를 구하였다. 검출한계와 정량한계는, Shrivastava와 Gupta의 방법[18]에 따라, 정량곡선 작성 시 사용된 가장 낮은 농도에서부터 순차적으로 5개의 농도의 표준편차를 정량곡선의 기울기로 나누어준 값에 각각 3.3과 10을 곱하여 얻은 값으로 하였다. 회수율 측정은 MEP가 들어있지 않음을 확인한 공시료(근육)에 MEP를 첨가하여 최종 농도가 1.0, 5.0, 10 ng/mL이 되도록 한 다음, 시료의 전처리 방법에 따라 3 반복 실험하였고, MEP 표준품의 pea k 면적에 대한 추출한 근육 시료의 pea k 면적비로부터 MEP의 회수율(%)을 구하였다. 또한, 회수율의 정밀성을 검증하기 위해, 3 반복 회수율로부터 상대표준편차를 구하였다. 측정된 정량한계, 회수율 그리고 상대표준편차는 식품의약품안전처의 잔류동물용의약품 분석법 실무 해설서 [19]에서 분석법 검증에 요구되는 정량한계 잔류허용기준의 1/2, 회수율 60-120% 그리고 상대표준편차 20-30% 이하를 검증 기준으로 적용하였다.
결 과
MEP의 크로마토그램
Fig. 1은 LC-MS/MS를 이용하여 MEP 표준용액(1.0 ng/mL)을 분석한 크로마토그램을 나타낸 것이다. MEP의 머무름 시간은 4.26분이었으며, 총 run time은 14분이었다. 양이온 모드에서 [M+H]+인 m/z 180.1이 기준이온(base ion)으로 검출되어 이를 선구이온(precursor ion)으로 선택 하였으며, product ion scan을 통하여 m/z 162.1 이온이 특성 이온으로 나타나 이들을 정성이온으로 선정하였다.
검량곡선, 검출한계 및 정량한계
본 시험에서, MEP의 표준용액을 0.1, 0.5, 1.0, 2.5, 5.0, 10.0 ng/mL의 농도로 조제하여 LC-MS/MS로 분석한 후 검량선의 직선성을 확인한 결과, 상관계수가 0.9974로 양호한 직선성을 나타내었다(Fig. 2). 또한, 본 시험방법에 따른 LC-MS/MS의 검출한계 및 정량한계는 각각 0.05 μg/kg 및 0.15 μg/kg이었다.
회수율과 정밀성
Table 1은 돼지 근육 시료에 MEP의 표준용액을 첨가한 후, 추출정제 방법과 기기분석 조건으로 3회 반복 분석 후, 회수율과 정밀성을 측정한 결과를 나타낸 것이다. 회수율과 상대표준편차의 범위는 각각 94.5-101.2%와 2.29-4.06%로 나타났다.
돼지 근육 중 MEP 잔류분석
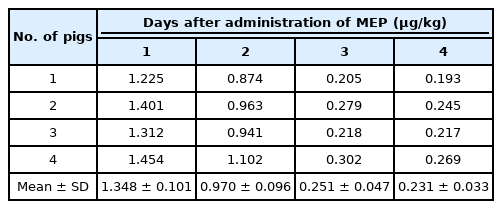
Table 2는 돼지에 MEP를 사료 톤 당 12 g을 혼합하여 7일 동안 연속해서 투여한 후, 경시별로 근육 시료를 채취하여, MEP 농도를 분석한 결과를 나타낸 것이다. MEP 투여 후, 1일째 근육 시료에서의 MEP의 농도는 식품공전 중 ‘동물용의약품의 잔류허용기준’(근육 0.01 mg/kg) 이하로 검출되었다 [20].
고 찰
본 연구에서는 MEP를 사료에 12 g/ton 농도로 혼합하여 돼지에 7일 동안 경구투여 후, 돼지 근육 중 MEP 잔류를 LC-MS/MS를 이용하여 분석하였다.
MEP 표준품에 대한 검량곡선은 0.9974의 상관계수를 나타내어 높은 직선성을 보였다. Zhang 등[16]은 돼지 근육과 우유 중 에서 MEP를 포함한 여러 종의 glucocorticoid 분석을 위해 확립한 LC-MS/MS법으로 MEP의 검량선을 작성한 다음, 직선성을 확인한 결과, 돼지 근육에서의 상관계수는 0.9906이었다고 보고하였다. 본 연구에서 얻은 MEP의 상관계수는 Zha ng 등[16]의 연구 결과와 비교하여 다소 높게 나타났다.
식품공전의 ‘식품 중 동물용의약품의 잔류허용기준’에 따르면[20], 돼지 근육 중 MEP의 최대잔류허용기준은 0.01 mg/kg으로 규정하고 있어서, 본 연구에서 확립한 MEP에 대한 잔류분석법은 돼지 근육 중 최대잔류허용기준 이하로 MEP의 잔류분석이 가능한 것으로 확인되었다. 식품의약품안전처의 잔류동물용의약품 분석법 실무 해설서의 식품에 대한 잔류동물용의약품 분석법 기준에 따르면[19], 잔류허용기준이 50 ng/mL 이하인 경우, 검출한계는 잔류허용기준의 1/2 이하이어야 하며, 정량한계는 10 ng/mL 이하이어야 한다고 규정하고 있다. 따라서 본 연구에서 확립한 검출한계(0.05 μg/kg)와 정량한계(0.15 μg/kg)는 잔류동물용의약품 분석법 실무 해설서의 분석기준을 충족하였다. Zhang 등 [16]의 연구에서, 돼지 근육 중 MEP의 검출한계와 정량한계는 각각 4와 10 μg/kg으로, 본 연구에서의 검출한계와 정량한계 보다 모두 높은 것으로 나타났다.
식품의약품안전처의 잔류동물용의약품 분석법 실무 해설서의 식품에 대한 잔류동물용의약품 분석법 기준에 따르면[19], 회수율의 검증기준은 1.0 μg/kg 이하의 농도에서는 50-120% 내에 있어야 하며, 1.0 μg/kg보다 크고 10 μg/kg 이하에서는 60-120% 내에 있어야 한다고 기준을 제시하고 있다. 또한, 상대표준편차는 1.0 μg/kg 이하의 농도에서는 35% 이하이어야 하며, 1.0 μg/kg보다 크고 10 μg/kg 이하에서는 30% 이하이어야 한다고 기준을 제시하고 있다. 본 연구에서 MEP의 회수율(94.5-101.2%)과 상대표준편차(2.29-4.06%)의 범위는 잔류동물용의약품 분석법 실무 해설서[19]에서 분석법 검증에 요구되는 검증기준을 모두 충족하는 것으로 조사되었다. Zhang 등[16]의 연구에서, 회수율과 상대표준편차의 범위는 각각 76.71-77.17%와 4.79-17.24%로, 본 연구의 회수율에 비해 낮았으며, 상대표준편차는 높은 것으로 나타났다.
이상의 연구결과로부터, 본 연구에서 제시한 LC-MS/MS에 의한 돼지 근육 중 MEP 정량분석법의 회수율, 상대표준편차, 검출감도 등은 식품의약품안전처의 잔류동물용의약품 분석법[19]의 기준을 모두 충족하는 것으로 나타났다. 또한. 기존 시험법에 비해 높은 회수율, 정밀성 그리고 검출감도를 갖고 있어서, 축산식품 중에 MEP의 신속한 분석이 가능할 것으로 판단된다. 아울러, 본 연구에서 MEP를 권장용량(12 g/ton feed, 7일)으로 투여한 결과, 1일째의 근육 시료 중 MEP의 농도가 동물용의약품의 잔류허용기준(근육 0.01 mg/kg) 이하로 검출되어, 돼지에서의 MEP의 적정 휴약기간은 0일로 설정하는 것이 합당할 것으로 사료된다.
Notes
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgements
본 논문은 ㈜ 중앙바이오텍(안산)의 지원에 의해 수행되었으며, 이에 감사드립니다.