 |
 |
| Korean J Vet Res > Volume 63(2); 2023 > Article |
|
Abstract
Acknowledgments
Fig.ô 1.
Tableô 1.
| Group |
Career area (n) |
Total (n, %) |
Pro-animal (AAS-5) |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cattle | Dairy cow | Pig | Chicken | Mixed | Sum (SD) | F(p) | ||
| Age (y) | 2.783* (0.043) | |||||||
| ãUnder 40s | 5 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 5 (1) | 19 (11.2) | 14.26a (2.88) | |
| ã40s | 4 | 2 | 14 | 2 | 11 (2) | 33 (19.4) | 16.39b (2.75) | |
| ã50s | 12 | 4 | 13 | 6 | 26 (1) | 61 (35.9) | 15.85b (3.32) | |
| ã60s | 21 | 10 | 3 | 2 | 21 | 57 (33.5) | 14.98a,b (3.00) | |
| Work experience (y) | 2.811* (0.041) | |||||||
| ãUnder 5 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 6 (2) | 16 (9.4) | 14.00a (2.22) | |
| ã5-10 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 3 (2) | 9 (5.3) | 16.33b (3.32) | |
| ã10-20 | 4 | 0 | 12 | 5 | 9 | 30 (17.6) | 16.57b (3.02) | |
| ãOver 20 | 31 | 15 | 19 | 5 | 45 | 115 (67.6) | 15.35a,b (3.15) | |
| ãTotal | 42 | 21 | 33 | 11 | 63 | 170 (100) | 15.54 (3.11) | - |
The number in parentheses in the ãcareer areaã column represents the number of women.
AAS-5, animal attitude scale-5 (5-point Likert score scale); SD, standard deviation.
Mean values sharing the same superscript letters (a, b) are not significantly different at p <0.05 based on a Duncanãs post-hoc analysis (post-hoc analysis: a < b).
Tableô 2.
| Statement | Answer choice | Response |
|---|---|---|
| Experience with educational information on PUA in one year (n = 170) | Yes | 84 (49.4) |
| No | 86 (50.6) | |
| Additional questions about the experience (n = 84, if yes) | ||
| ãInformation channels* | TV/radio/newspaper | 14 (16.7) |
| PUA poster/brochure | 36 (42.9) | |
| Educational program (offline) | 39 (46.4) | |
| Educational program (online) | 26 (31.0) | |
| SNS/Youtube | 15 (17.9) | |
| Others | 6 (7.1) | |
| ãSource of information* | Ministry of Agriculture, Forest, Livestock and Food | 36 (42.9) |
| Ministry of Health | 4 (4.8) | |
| Fellow veterinarians | 3 (3.6) | |
| Domestic veterinary association | 53 (63.1) | |
| International veterinary association | 6 (7.1) | |
| Veterinary pharmaceutical companies | 15 (17.9) | |
| Academia | 14 (16.7) | |
| Others | 4 (4.8) | |
| ãDegree of change in behavior | Never changed | 2 (2.4) |
| Little changed | 16 (19.1) | |
| Somewhat changed | 60 (71.4) | |
| Totally changed | 6 (7.1) |
Tableô 3.
| Variable | Item | Totally disagree | Disagree | Agree | Totally agree |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PUA-belief (CöÝ = 0.691) | Antimicrobials used for livestock should be prescribed by a veterinarian. | 0 (0) | 7 (4.1) | 61 (35.9) | 102 (60.0) |
| It is important to maintain the prescribed dose and route for antimicrobials. | 0 (0) | 3 (1.8) | 78 (45.9) | 89 (52.4) | |
| PUA is more important than cost-benefit considerations. | 1 (0.6) | 4 (2.4) | 90 (52.9) | 75 (44.1) | |
| It is a duty for veterinarian to reduce the use of antimicrobials. | 4 (2.4) | 24 (14.1) | 90 (52.9) | 52 (30.6) | |
| My income will decrease if antibiotics are used against the farmerãs wishes* | 44 (25.9) | 81 (47.6) | 36 (21.2) | 9 (5.3) | |
| PUA-self efficacy (CöÝ = 0.716) | I can acquire enough information about PUA as I needed. | 2 (1.2) | 32 (18.8) | 104 (61.2) | 32 (18.8) |
| I can prescribe proper antimicrobials for livestock diseases according to the diagnosis. | 0 (0) | 2 (1.2) | 119 (70.0) | 46 (27.1) | |
| I have a plan for reducing antimicrobial use during my practice. | 3 (1.8) | 51 (30.0) | 92 (54.1) | 24 (14.1) | |
| I can exclude the antimicrobials for livestock which are often used for human medical use. | 10 (5.9) | 48 (28.2) | 94 (55.3) | 18 (10.6) | |
| I can educate livestock farmers about PUA. | 1 (0.6) | 22 (12.9) | 111 (65.3) | 36 (21.2) |
Tableô 4.
| Statement | Answer choice | Response |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency of antimicrobials susceptibility test prior to use (n = 170) | Never | 42 (24.7) |
| Rarely | 89 (52.4) | |
| Often | 37 (21.8) | |
| Always | 2 (1.1) | |
| Reasons never/rarely conduct antimicrobials susceptibility test (n = 131) | Farmers feel the test is unnecessary. | 38 (29.0) |
| Farmers feel financial pressure for the test. | 32 (24.4) | |
| The test cannot ensure a successful outcome. | 23 (17.6) | |
| I am unsure of how to request the test. | 11 (8.4) | |
| Others | 27 (20.6) | |
| How to choose antimicrobials (n = 170)* | The same products previously used | 79 (46.5) |
| Academic guidelines | 72 (42.4) | |
| Recommendations from colleagues | 29 (17.1) | |
| Refer to the efficacy of the product advertising | 27 (15.9) | |
| Guidelines of veterinary associations | 26 (15.3) | |
| Recommendation of veterinarians at a pharmaceutical companies | 25 (14.7) | |
| Others | 27 (15.9) |
Tableô 5.
Tableô 6.
Tableô 7.
| Variable |
Model 1 |
Model 2 |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| öý | t | VIF | öý | t | VIF | |
| (Constant) | 11.992 | 3.809 | ||||
| ãDemographics | ||||||
| ããAge_year | -0.294* | -2.611 | 2.218 | -0.158 | -1.548 | 2.426 |
| ããExperience_year | 0.308** | 2.814 | 2.105 | 0.141 | 1.416 | 2.315 |
| ããAAS-5 | 0.077 | 1.002 | 1.035 | 0.013 | 0.19 | 1.078 |
| ãCareer Area (cattle = ref.) | ||||||
| ããDairy cow | 0.001 | 0.006 | 1.341 | -0.011 | -0.143 | 1.38 |
| ããPig | 0.062 | 0.65 | 1.586 | -0.035 | -0.412 | 1.65 |
| ããChicken | 0.041 | 0.499 | 1.195 | -0.026 | -0.359 | 1.235 |
| ããMixed | -0.072 | -0.755 | 1.577 | -0.066 | -0.804 | 1.59 |
| ãPUA-education (yes = 1) | 0.174* | 2.586 | 1.057 | |||
| ãPUA-belief | 0.161* | 2.036 | 1.467 | |||
| ãPUA-self efficacy | 0.383*** | 4.704 | 1.547 | |||
| R2 | 0.088 | 0.327 | ||||
| adjR2 | 0.048 | 0.284 | ||||
| F | 2.215* | 7.636*** | ||||
Tableô 8.
| IV | DV | B | SE | öý | t | F | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
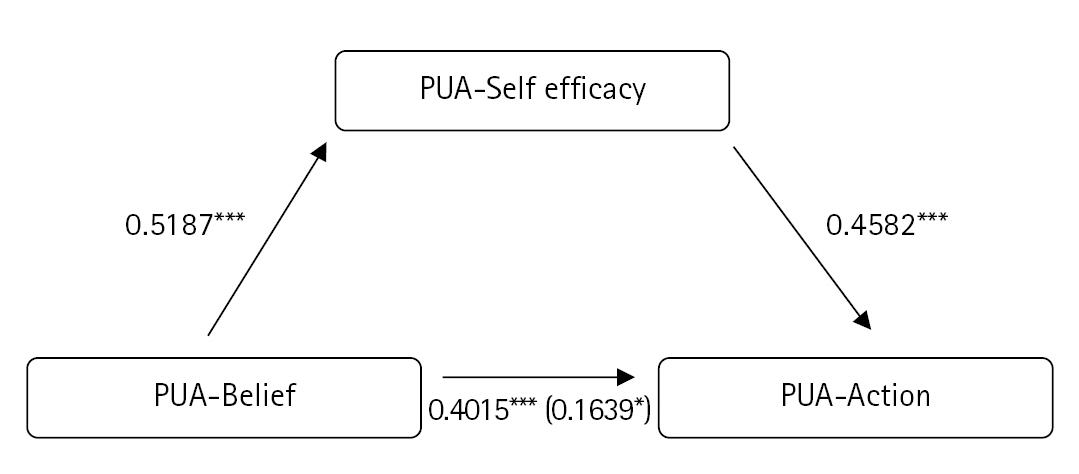
| PUA-belief | PUA-self efficacy | 0.5187 | 0.0699 | 0.5024 | 7.4179*** | 55.0255*** | 0.2524 |
| PUA-belief | PUA-action | 0.4015 | 0.0782 | 0.3732 | 5.1357*** | 26.375*** | 0.1393 |
| PUA-belief | PUA-action | 0.1639 | 0.0827 | 0.1523 | 1.9807* | 32.0974*** | 0.2838 |
| PUA-self efficacy | 0.4582 | 0.801 | 0.4397 | 5.7177*** |
References
- TOOLS
-
METRICS

- ORCID iDs
-
Yoojin Choi

https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3837-1216Seola Joo

https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5024-8448Sang-Won Lee

https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1956-7245Hong-Jae Lee

https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9788-177XMyung-Sun Chun

https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0658-2895 - Related articles


 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print



